If an organisation of info. system is hosting information, are they responsible for the content?
Google Executives jailed in Italy
In Italy, three Google executives have been found guilty and given six month suspended sentences because of a video that shows the mistreatment of a boy with Down Syndrome.
[Reasons and arguments why prosecutors thought google was liable]
Prosecutors argued that Google execs were negligent; not responding to requests to take down the video
Google hosts YouTube, therefore there is a question to are they responsible for the content/
Google's defence- that the execs had nothing to do with the video and that it is almost imopossible to review every single frame in a video to permit it to be uploaded online
Facebook urged to act after memorial sites defaced
Premier of QLD, Anna Bligh, has written a letter to Facebook to review memorial pages on its site after a case of a young girl's memorial page being defaced by certain people.
Thursday, February 25, 2010
Tuesday, February 23, 2010
Tools for transmitting and receiving
Binary digits- 0s and 1s
Serial data transmission- a form of data transmission in which the bits of each character are sent one at a time along a single communication path [one path] eg. mouse, USB- Universal Serial Bus, Internet
Parallel transmission data- a form of data transmission in which the bits of each character are all sent simultaneously, resulting in extrememly fast communication but requiring a communication path for each bit.
[8 paths] eg. some printers with parallel port
Signal Direction
Simplex- data links that allow the data to move in one direction. In a simplex link there is no need for a return data signal [one way communication] eg. radio, traditional free-to-air television
Half Duplex- data links that allow the data to move in both directions, but not at the same time [one way at a time] eg. UHF radio
Full Duplex- (also known as duplex) data links allow the data to move simultaneously in both directions. [Both devices in the link must be able to send and receive at the same time] eg. mobile phones, landline telephones
Serial data transmission- a form of data transmission in which the bits of each character are sent one at a time along a single communication path [one path] eg. mouse, USB- Universal Serial Bus, Internet
Parallel transmission data- a form of data transmission in which the bits of each character are all sent simultaneously, resulting in extrememly fast communication but requiring a communication path for each bit.
[8 paths] eg. some printers with parallel port
- faster, but over longer distances the data goes out of sync and takes a longer time to arrive, therefore serial is preferred over longer distances
Signal Direction
Simplex- data links that allow the data to move in one direction. In a simplex link there is no need for a return data signal [one way communication] eg. radio, traditional free-to-air television
Half Duplex- data links that allow the data to move in both directions, but not at the same time [one way at a time] eg. UHF radio
Full Duplex- (also known as duplex) data links allow the data to move simultaneously in both directions. [Both devices in the link must be able to send and receive at the same time] eg. mobile phones, landline telephones
 Synchronous- communication links use agreed times for data to be transmitted and received [happen at the same time- real time] eg. phone calls, skype, text chat, dedicated video conference
Synchronous- communication links use agreed times for data to be transmitted and received [happen at the same time- real time] eg. phone calls, skype, text chat, dedicated video conference
Asynchronous- no set time for the data to be transmitted or received [out of time-delayed] eg. text message, e-mails, blogs, forums, podcasts, videoblogs
Useful links: http://learningwithcomputers.pnworks.com/Synchronous-Communication
Google 'examples of synchronous communications csu hsc edu' and open powerpoint
Data Signals
Bandwith- the number of bits moving at any given time
Baud- transmission cycle; every transmission occurs in a cycle or transmissions per cycle; how times per second data(bits) is transmitted
Saturday, February 20, 2010
Diagrams of an information systems
Mastery Test Ch.1
Multiple Choice
1. A system is (c) a collection of parts that work together
2. An information system system (a) turns data into information
3. A person who attributes data to an info. system but is not involved in its operation and does not use any info. or data it produces is (c) in the system environment
4. The environment of an information systems (d) describes where it used
5. The info. technology of an information systems is (b) its equipment and instructions
6. A personal info.system (c) is designed for use by individuals
7. Which part of an info. systems will end users find most useful?
(a) data and information
8. Which list contains all the categories that would be needed to adequately describe the role of an info. system?
(c) data/information, purpose. info. processes
9. The participants [eg.web designers, software engineers, data entry operators] in an information system (a) are responsible for its operation
10. A home PC is an example of (d) a generalized info. system
Fill in the blanks
11. A system is a collection of parts that work together to achieve a particular purpose or result
12. All systems have inputs, processes and outputs [IPO diagrams]
13. An information system accepts data as an input and produces information or processed data as an output
14. Every system has a purpose that describes why it is needed and an environment where it is used
15. Information technology is the equipment (hardware) used by an info system and the instructions (software) that control the equipment
16. A participant is anyone who is involved in the operation or running of an info system
17. Info. systems depend on their environment for data
18. An end user is the person who receives the info. produced by an info system
19. The environment is where an info system is used by many different participants
20. A group information systems is used by many different participants
Match the terms
1. G
2. D
3. A
4. F
5. C
6. J
7. A
8. B
9. E
10. H
22. Identify the info technology and participants in a computerised library catalogue/ circulation info system.
-Computer, barcode scanner, books, barcodes, data-entry operator, librarian
23. Explain how new developments in technology have influenced info. systems
- Has caused higher expecation ad greater needs by many individuals
[eg. iPod- music can be accessed anywhere and downloaded at any place provided there is Wi Fi
Netbooks - quick and easy access to internet
Web 2.0- placing applications online, only need of browser to access applications, not necessarily online]
24. Describe how computer-based IT has altered the roles of participants in info. systems
- eliminated tedious tasks
- machines replace humans
- end users become data-entry operators
25. Justify that computer-based info. systems have become a vital point of our lifestyles
- used for various tasks inclding online banking, online shopping, means of communcation and research etc.
26. Contrast the roles of end users in personal and group info. systems
- full control over limited control
- not shared over shared information
1. A system is (c) a collection of parts that work together
2. An information system system (a) turns data into information
3. A person who attributes data to an info. system but is not involved in its operation and does not use any info. or data it produces is (c) in the system environment
4. The environment of an information systems (d) describes where it used
5. The info. technology of an information systems is (b) its equipment and instructions
6. A personal info.system (c) is designed for use by individuals
7. Which part of an info. systems will end users find most useful?
(a) data and information
8. Which list contains all the categories that would be needed to adequately describe the role of an info. system?
(c) data/information, purpose. info. processes
9. The participants [eg.web designers, software engineers, data entry operators] in an information system (a) are responsible for its operation
10. A home PC is an example of (d) a generalized info. system
Fill in the blanks
11. A system is a collection of parts that work together to achieve a particular purpose or result
12. All systems have inputs, processes and outputs [IPO diagrams]
13. An information system accepts data as an input and produces information or processed data as an output
14. Every system has a purpose that describes why it is needed and an environment where it is used
15. Information technology is the equipment (hardware) used by an info system and the instructions (software) that control the equipment
16. A participant is anyone who is involved in the operation or running of an info system
17. Info. systems depend on their environment for data
18. An end user is the person who receives the info. produced by an info system
19. The environment is where an info system is used by many different participants
20. A group information systems is used by many different participants
Match the terms
1. G
2. D
3. A
4. F
5. C
6. J
7. A
8. B
9. E
10. H
22. Identify the info technology and participants in a computerised library catalogue/ circulation info system.
-Computer, barcode scanner, books, barcodes, data-entry operator, librarian
23. Explain how new developments in technology have influenced info. systems
- Has caused higher expecation ad greater needs by many individuals
[eg. iPod- music can be accessed anywhere and downloaded at any place provided there is Wi Fi
Netbooks - quick and easy access to internet
Web 2.0- placing applications online, only need of browser to access applications, not necessarily online]
24. Describe how computer-based IT has altered the roles of participants in info. systems
- eliminated tedious tasks
- machines replace humans
- end users become data-entry operators
25. Justify that computer-based info. systems have become a vital point of our lifestyles
- used for various tasks inclding online banking, online shopping, means of communcation and research etc.
26. Contrast the roles of end users in personal and group info. systems
- full control over limited control
- not shared over shared information
Sunday, February 14, 2010
Social and Ethical Issues
Privacy and security- data can be shared quickly between large no. of different information systems. At each system any no. of users may have access to the data. This puts private and confidential information at risk of being misusesd and abused. Data must be protected against accidental or deliberate damage.
Access and control- without communication systems, such as the Internet and telephone network, there would be little or no flow of info. to users. Controllers of systems, control the information. Linked with equity; for eg. students in regional area who do not have broadband access may be disadvantaged in terms of preparing for HSC OR pensioners who have to pay bills online because a surplus fee is added for
Employment and the changing nature of work- those with lack of information skills and cannot use new technology become at risk of unemployment. In an effort to compete in the global market, industries may be forced to downsize their workers and automate their manufacturing operations. Even workers in high-technology jobs will have to constantly retrain to keep their skills and jobs.
-Telecommuting- working at home; miss out on social interaction, more distractions, like looking after children
Access and control- without communication systems, such as the Internet and telephone network, there would be little or no flow of info. to users. Controllers of systems, control the information. Linked with equity; for eg. students in regional area who do not have broadband access may be disadvantaged in terms of preparing for HSC OR pensioners who have to pay bills online because a surplus fee is added for
Employment and the changing nature of work- those with lack of information skills and cannot use new technology become at risk of unemployment. In an effort to compete in the global market, industries may be forced to downsize their workers and automate their manufacturing operations. Even workers in high-technology jobs will have to constantly retrain to keep their skills and jobs.
-Telecommuting- working at home; miss out on social interaction, more distractions, like looking after children
Sunday, February 7, 2010
Data and Information
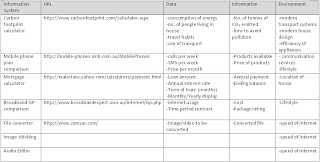
1. For each of the scenarios in the table below, locate an informtion system and then complete the table;
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)









